Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) have evolved significantly, transforming how all organizations manage their workforce. In 2025, businesses are leveraging advanced technologies like AI, automation, and cloud-based solutions to enhance HR processes. In this guide, we’ll explore what HRMS is —its definition, benefits, features, trends, and implementation—to help you make informed decisions about HRMS adoption. Whether you’re a growing company or an enterprise looking for HR management software in India, understanding the latest tools and strategies is essential for effective workforce management.
What is HRMS?
What does HRMS stand for?
An HRMS stands for Human Resource Management System, a comprehensive software solution intricately designed to streamline and automate various HR functions within an organization. It integrates multiple HR processes into a unified platform, improving efficiency, accuracy, and employee experience.
History of Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS):
Human Resource Management Systems have evolved from informal labour management in the pre-industrial era to the rise of computerized payroll calculation mechanisms.

Source- Google
Here is the complete history of how HRMS evolved.
- Pre-Industrial Era– Labor management was focused on a community-based approach.
- Industrial Revolution– Due to mass production, systematic workforce management began. New welfare roles were also introduced to protect workers.
- Early 20th Century– Increased workforce diversity with women joining industries led to formal roles for recruitment, dismissal, and employee relations.
- Computerization Era– The first computerized payroll system to automate clerical tasks.
- Introduction of Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS)– Development of systems to manage job applications more efficiently.
- First HRMS Introduced– Integration of various HR functions into cohesive systems was first introduced in the 1980s.
- Modern HRMS Development—The SAP R/2 launch integrates HR with other business functions. Plus, there was a transition to web-based systems for broader access and employee self-service functionalities.
- Digital Transformation Era– Switching to cloud Human Resource Management System with AI cuts costs and implementation time by removing on-premises infrastructure. AI improves recruitment, engagement, and analytics.
Core Functions of an HRMS:
An HRMS covers essential HR operations, including:
A. Employee Data Management
- Stores employee details such as demographics, job roles, salaries, and performance records.
- Ensures centralized and secure access to HR data.
B. Payroll & Compensation Management
- Automates salary calculations, tax deductions, and compliance with the labor laws.
- Ensures timely payments and reduces errors in payroll processing.
C. Recruitment & Applicant Tracking
- Streamlines hiring by posting job listings, screening resumes, and scheduling interviews.
- Tracks applicants’ progress throughout the recruitment process.
D. Attendance & Leave Management
E. Performance Management
- Tracks employees’ key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Facilitates goal setting, feedback, and performance reviews.
F. Learning & Development
- Provides access to the training programs and skill development courses.
- Tracks progress and certifications for employee growth.
G. Compliance & Regulatory Management
- Ensures adherence to labor laws, tax regulations, and workplace policies.
- Generates reports for audits and legal compliance.
Also Read: Exploring How an HRMS Payroll Management System Drives Away Your Pay-Day Fears
Who Uses HRMS Software?
Here are some of the major stakeholders that use HRMS software.
A. HR Professionals:
As an HR professional, you can use HRMS to lessen manual tasks and improve focus on strategic policies. Your administrative load reduces significantly as you automate repetitive tasks like leave approvals and data entry. You obtain very valuable insights through in-depth reports and analytics, enabling you to guide your management on important workforce decisions.
B. Department Managers:
As a department manager, you can access all employee information and manage your team efficiently without endless HR intervention using HRMS. This information can include performance monitoring, employee attendance, and task schedules. You can make well-informed decisions regarding resource allocation and employee development using real-time information.
C. Employees:
Using self-service portals can improve the employee work experience. Employees can easily request leaves, change details, and view benefit information. They can also connect more closely with your company through immediate access to training options and performance guidance.
Why is HRMS important?
HRMS (Human Resource Management System) is essential for the organizations and businesses because it streamlines HR operations, improves efficiency, and enhances employee experience. 80% of HRs strongly feel that using HR technology has helped them improve employee attitude towards the company. Here’s why this is crucial:
1. Automates Administrative Tasks
- Human Resource Management System automates repetitive tasks like payroll processing, attendance tracking, and benefits management, reducing the workload for HR teams.
2. Enhances Employee Experience
- With the self-service portals, employees can access their payroll details, request leaves, and update all crucial information, leading to greater satisfaction and engagement.
3. Improves Compliance & Security
- HRMS helps all businesses comply with the labor laws, tax regulations, as well as workplace policies by automatically tracking legal requirements and securing employee data.

Source: Google
4. Streamlines Recruitment & Onboarding
- HRMS facilitates job postings, applicant tracking, and digital onboarding, making hiring process more efficient and reducing time-to-hire.
5. Provides Data-Driven Insights
- Advanced analytics that help the HR managers track workforce trends, optimize resource allocation processes, and boost employee productivity.
6. Reduces Costs
- Businesses can cut operational costs, minimize errors, and ensure efficient workforce management by automating HR processes.
7. Supports Remote & Hybrid Workforces
- Cloud-based Human Resource Management System allows employees to access HR services remotely, ensuring smooth workforce management in a digital work environment.
- Human Resource Management System is more than a tool—it’s a strategic asset for businesses looking to modernize HR operations and optimize their workforce. Would you like insights on choosing the right HRMS for your business? Let me know!
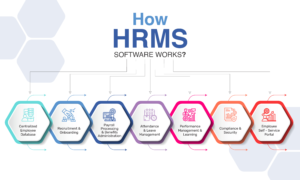
How HRMS Software Works?
HRMS (Human Resource Management System) software automates and manages various HR functions, improving efficiency, compliance, and employee satisfaction. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how HRMS software operates:
1. Centralized Employee Database
HRMS stores all employee-related data, including the personal details, job roles, salaries, performance history, as well as benefits. This centralized database eliminates manual record-keeping and also ensures easy access to accurate information.
2. Recruitment & Onboarding
- Job Posting & Applicant Tracking
- HRMS helps HR teams post job vacancies on multiple platforms.
- AI-powered tools screen resumes and rank applicants based on criteria.
- Interview scheduling and candidate evaluation are streamlined.
Digital Onboarding
- New hires receive automated onboarding tasks and training modules.
- Documents like contracts and policies are digitally signed and stored in the system.
3. Payroll Processing & Benefits Administration
HRMS automates salary calculations, tax deductions, and compliance management.
Payroll Management
- Automatically calculates employee salaries, overtime, and deductions.
- Ensures compliance with tax regulations and benefits policies.
- Generates pay slips and direct deposit transfers.
Benefits & Compensation
- Employees can enroll in the health insurance, retirement plans, and the other benefits through a self-service portal.
- Tracks bonuses, raises, and incentive programs.
Source: SFT Evolve
4. Attendance & Leave Management
HRMS eliminates manual time-tracking by integrating with biometric devices, mobile apps, and online portals.
Time Tracking
- Employees clock in and out using biometric scanners or mobile applications.
- HRMS records work hours, overtime, and breaks for payroll processing.
Leave Management
- Employees request leave digitally, which HR can approve or modify instantly. So, this is helpful for leave management as well.
- Human Resource Management System ensures compliance with leave policies and also tracks vacation balances.
5. Performance Management & Learning
HRMS helps organizations monitor employee performance, provide feedback, and encourage growth.
Goal Setting & Evaluation
- HRMS enables managers to set and track performance goals.
- Automated feedback systems streamline performance review cycles.
Training & Learning Management
- Employees enroll in training courses directly through the system.
- Certifications and skill development are tracked.
6. Compliance & Security
HRMS ensures compliance with labor laws, tax regulations, and company policies.
Regulatory Compliance
- HRMS generates reports for audits and compliance checks.
- Tracks employee contracts and legal documentation.
Data Security
- Encryption and multi-factor authentication protect sensitive employee data.
- Role-based access controls ensure that only the authorized personnel can view critical information.
7. Employee Self-Service Portal
HRMS empowers the employees to manage their records.
Features:
- Access pay slips, benefits, and leave balances anywhere, anytime.
- Update personal details without needing HR intervention.
- Submit HR-related requests and receive the instant responses.
Key Features of Modern HRMS:
Modern Human Resource Management System solutions incorporate the highly advanced features to enhance their efficiency and data-driven decision-making:
A. Cloud-Based Accessibility
- Permits the HR teams and employees to access HRMS remotely.
- Ensures scalability and strengthened data security.
B. AI & Machine Learning Integration
- AI-driven insights help HR teams predict workforce trends.
- Automates repetitive tasks like resume screening and payroll processing.
C. Employee Self-Service Portals
- Employees can update personal details, request leave, and access pay slips.
- Reduces HR workload by empowering employees.
D. Mobile Compatibility
- HRMS apps enable employees to manage HR tasks on smartphones.
- Facilitates remote work and real-time updates.
E. Advanced Analytics & Reporting
- Generates reports on overall employee performance, workforce planning, and HR trends.
- Helps HR managers make informed decisions.
F. Integration with Other Business Tools
- Connects seamlessly with the accounting software, CRM, and project management tools.
- Ensures effortless workflow across different departments.
Also Read: The Smart HR Solution to Empower Your Business
SFT Evolve- the ultimate HRMS for all:
SFT Evolve is a comprehensive end-to-end HRMS designed to streamline human resource management for businesses of all sizes. It offers advanced features covering every crucial aspect of HR operations, ensuring efficiency, compliance, and employee satisfaction.
Source: SFT Evolve
Key Features of SFT Evolve HRMS:
Onboarding & Recruitment
- Simplifies hiring with collaborative tools for candidate screening and onboarding.
- Supports unlimited job postings on company websites and third-party career portals.
Performance Management
- Provides 360-degree feedback for effective employee evaluations.
- Encourages frequent and topical performance reviews to enhance workforce productivity.
Attendance & Leave Management
- Tracks employee attendance, breaks, and time-off requests.
- Offers a flexible leave management system with real-time monitoring and approvals.
Payroll Management
- Automates salary calculations, tax deductions, and compliance tracking.
- Ensures accurate payroll processing with integrated financial management tools.
Employee Self-Service Portal
- Allows employees to access personal records, request leave, and manage HR-related tasks.
- Enhances transparency and engagement by empowering employees with self-service options.
Compliance & Security
- Ensures adherence to labor laws and workplace regulations.
- Uses facial recognition technology for secure employee time tracking.
Mobile Accessibility
- Offers a mobile and web application for seamless HR management on the go.
- Enables employees to clock in/out, access pay slips, and update profiles via mobile devices.
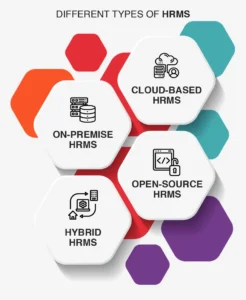
What are the different types of HRMS?
HRMS solutions come in various types, each catering to different business needs, scalability requirements, and IT infrastructure preferences. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the common types of HRMS:
1. On-Premise HRMS
An on-premise HRMS is installed locally on a company’s servers and is managed by its IT team.
Features:
- Full control over customization and data security.
- Requires internal IT support for maintenance and updates.
- One-time licensing cost with periodic maintenance expenses.
Best For: Large enterprises and organizations with strict data security policies or regulatory requirements.
Challenges: Higher upfront costs, complex installation, and dependency on in-house IT teams for upgrades.
2. Cloud-Based HRMS
A cloud-based HRMS is hosted on a vendor’s server and accessed online.
Features:
- Easy access from anywhere via web or mobile applications.
- Subscription-based pricing (monthly or annual fees).
- The vendor handles automatic updates and maintenance.
Best For: Small to medium-sized businesses, startups, and enterprises looking for scalability and flexibility.
Challenges: Requires internet connectivity; some companies may have concerns about data privacy.
Source: SFT Evolve
3. Hybrid HRMS
A hybrid HRMS combines elements of both on-premise and cloud-based HRMS, offering flexibility.
Features:
- Critical HR functions remain on-premise, while other features are cloud-based.
- Provides better customization options than fully cloud-based Human Resource Management System.
- Enhanced security with selective cloud integration.
Best For: Companies transitioning from legacy systems to cloud solutions while maintaining certain critical data on-premise.
Challenges: Can be complex to manage due to dual infrastructure.
4. Open-Source HRMS
An open-source HRMS allows businesses to customize and modify the software freely.
Features:
- No licensing fees; businesses can tailor functionality as needed.
- Requires in-house IT expertise for customization and maintenance.
- Community-driven updates and support.
Best For: Tech-savvy businesses that need a fully customizable HRMS solution.
Challenges: Higher dependency on IT staff and security risks with third-party modules.
5. Industry-Specific HRMS
Some HRMS solutions are tailored for specific industries, such as healthcare, retail, or manufacturing.
Features:
- Pre-configured templates for industry-specific HR workflows.
- Compliance with niche labor laws and regulations.
- Features optimized for sector-specific needs (e.g., scheduling tools for healthcare).
Best For: Companies with unique HR requirements that general HRMS solutions do not address.
Challenges: May not be scalable outside of the specific industry it caters to.
Also Read: Cost vs Value: Is Your HRMS Saving You Money?
Which HRMS Type is Right for You?
- Choose On-Premise if security and full control are critical.
- Go for Cloud-Based if flexibility, scalability, and low maintenance are priorities.
- Opt for Hybrid if you need a mix of cloud access with sensitive on-premise storage.
- Consider Open-Source if customization is a priority and you have strong IT support.
- Industry-specific HRMS is ideal if your business has specialized HR needs.
HRMS vs. HRIS vs. HCM
Understanding the differences between HRMS, HRIS (Human Resource Information System), and HCM (Human Capital Management) is crucial:
- HRIS focuses on storing employee data and managing basic HR tasks.
- HCM covers broader aspects of talent management and workforce optimization.
- HRMS combines HRIS and HCM functionalities, offering end-to-end workforce management.
Navigating the differences between HRIS, HRMS, and HCM is crucial for organizations looking to optimize their HR processes and strategies. Organizations can enhance efficiency, improve employee engagement, and drive strategic business outcomes by choosing the right system.
Comparison Summary
| Feature |
HRMS (Complete HR System) |
HRIS (Data & Payroll System) |
HCM (Strategic Workforce Management) |
| Employee Data Management |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
| Payroll & Compensation |
✅ |
✅ |
❌ |
| Attendance & Leave |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
| Talent Acquisition |
✅ |
❌ |
✅ |
| Performance Management |
✅ |
❌ |
✅ |
| Learning & Development |
✅ |
❌ |
✅ |
| Compliance & Reporting |
✅ |
✅ |
❌ |
| AI & Predictive Analytics |
✅ |
❌ |
✅ |
What are the common challenges in HRMS implementation?
Implementing an HRMS can be transformative, but it comes with challenges. Here are some common obstacles businesses face:
1. Resistance to Change
Employees accustomed to traditional HR processes may resist adopting new technology. Clear communication and training can help ease the transition.
2. Data Migration Issues
Transferring data from legacy systems to a new HRMS can be complex, leading to errors or incomplete records. A structured migration plan and thorough testing are essential.
3. Integration Challenges
HRMS must integrate seamlessly with existing software, such as payroll and accounting systems. If compatibility issues are not addressed early, they can disrupt workflows.
4. Lack of Employee Training
Employees may struggle to use the new system effectively without proper training, leading to inefficiencies and frustration.
5. Ensuring Data Security
HRMS stores sensitive employee data, making security a top priority. Businesses must implement strong encryption and access controls to prevent breaches.
6. Poor Vendor Support
Inadequate vendor assistance can lead to unresolved technical issues and slow adoption. Therefore, it is crucial to choose a reliable vendor with strong customer support.
7. Compliance & Legal Issues
HRMS must comply with labor laws and data protection regulations. Failure to do so can result in legal penalties and operational setbacks.
Would you like insights on how to overcome these challenges effectively? I can provide best practices for a smooth HRMS implementation!
Latest Trends in HRMS:
A. AI & Predictive Analytics
Machine learning algorithms analyze workforce trends and suggest actionable insights for improving employee retention.
B. Cloud-Based Solutions
More businesses are moving to cloud-based HRMS for scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness.
C. Mobile-Friendly HRMS Platforms
With the rise of remote and hybrid work models, HRMS solutions now offer mobile applications for employees to access HR functions on the go.
D. Blockchain for Security
Blockchain technology is improving data security and ensuring immutable records for employee transactions.
Key benefits of HRMS for various stakeholders:
A. Human resources department:
HRMS allows HR managers to automate workflows and focus on other tasks that require more attention and interaction.
B. Organizations:
With all the paperwork taken care of, companies have more time to focus on hiring candidates and employees, allowing them to expand faster. This increases the company’s productivity and leads to higher revenue.
C. Employees:
Employees can use the Employee Self-Service page to receive notifications and edit their profiles, helping to reduce misunderstandings and promote higher levels of engagement and satisfaction.
How to Implement HRMS Successfully?
Key factors to consider when selecting the right HRMS:
- Business size and HR needs
- Integration capabilities
- Data security measures
- Scalability for future growth

Source: Google
Overcoming Implementation Challenges:
Common challenges include employee resistance to change, data migration complexities, and software integration issues. A well-planned rollout strategy, proper training, and vendor support can ensure a smooth transition.
Future of HRMS:
As AI, automation, and data analytics evolve, HRMS systems will become even more sophisticated, reducing HR workload while improving employee experiences. Future innovations may include advanced virtual assistants, deeper AI-driven insights, and hyper-personalized workforce management tools.
Why Choose SFT Evolve?
- Scalable & Customizable: Adapts to unique business needs with flexible configurations.
- Cloud-Based & Secure: Provides remote access while ensuring data security.
- User-Friendly Interface: Simplifies HR processes with an intuitive dashboard.
SFT Evolve is a powerful HRMS solution that helps businesses optimize workforce management, improve employee engagement, and ensure compliance. You can explore more details on their official website.
Pro Tip: Pricing Starts at ₹40 per employee per month, approximately!
Conclusion:
In 2025, HRMS is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses. Its ability to streamline HR functions, enhance employee satisfaction, and ensure compliance makes it an indispensable tool. Implementing a Human Resource Management System (HRMS) can revolutionize your business’s HR processes. With continuous advancements in AI and cloud computing, HRMS will play a crucial role in shaping the future of HR management.







